Building automation systems (BAS) are transforming the way we manage and operate buildings. They integrate various systems like HVAC, lighting, and security into a single, centralized control.
This technology is not just about convenience. It's about efficiency, sustainability, and cost savings.
From controlling the temperature to managing smart lighting, BAS are becoming the backbone of modern buildings. They are the key to unlocking the full potential of embedded technology in our structures.
In this article, we will delve into the world of building automation. We'll explore its components, benefits, and the technology that drives it.
We'll also look at how top building automation companies are innovating in this space. Whether you're a facility manager, a building owner, or just interested in smart building technology, this article is for you.
Join us as we journey from HVAC control to smart lighting with embedded tech in building automation.
Introduction to Building Automation
Building automation is revolutionizing how we interact with the buildings we live and work in. At its core, building automation refers to the automatic centralized control of a building's various systems. This includes environmental, security, and communications systems. These systems are integrated into a network that can be easily managed through a central interface.
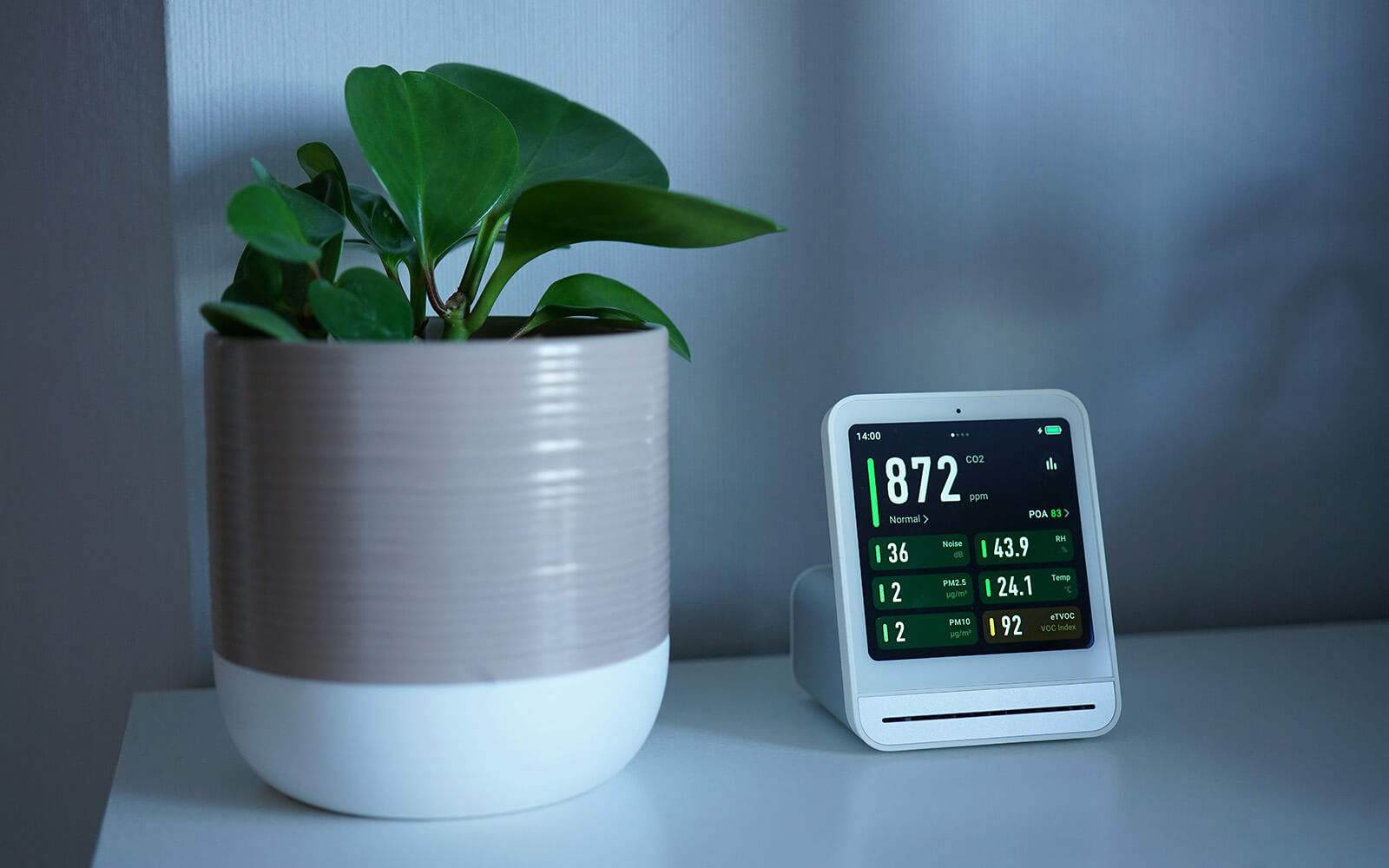
Energy management is a key aspect of building automation. With rising energy costs and environmental concerns, optimizing energy use is crucial. Automation allows for better control over heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, leading to significant energy savings.
Furthermore, building automation enhances occupant comfort and safety. It enables better indoor climate control and integrates advanced security measures. Automated systems can detect issues and faults early, allowing for preventative maintenance. This means fewer disruptions and lower operating costs over time.
Automation is a growing industry, with significant advancements each year. The development of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has further accelerated growth. IoT allows devices to communicate and make decisions in real-time, enhancing the capabilities of automation systems.
Overall, building automation not only supports sustainability but also improves the user experience. It creates smarter, more responsive buildings that can adapt to the needs of their occupants.
Definition of Building Automation Systems
Building automation systems (BAS) are advanced control systems managing a building's core functions. These systems include mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems. BAS improve operations through the centralized control of heating, cooling, lighting, and security. It is an integration of different technologies that ensures optimal performance and efficiency.
The system automates routine tasks, making buildings smart and adaptive. This technology aligns with modern sustainability goals by reducing energy waste and lowering operational costs. BAS stands as a cornerstone for efficient building management.
Importance of Automated Building Controls
Automated building controls are crucial in modern architecture and facility management. These controls are fundamental to maintaining ideal operational conditions. They ensure that HVAC, lighting, and security systems work seamlessly, improving efficiency and sustainability.
Automated controls reduce human error and allow for precise management of building systems. For instance, automated HVAC systems adjust temperatures in real-time based on occupancy and weather conditions. This not only conserves energy but also enhances occupant comfort.
Lighting automation also plays a significant role in energy management. By using sensors and timers, lighting can adjust according to natural light availability and usage patterns. This results in significant energy savings and prolonged lifespan of lighting fixtures.
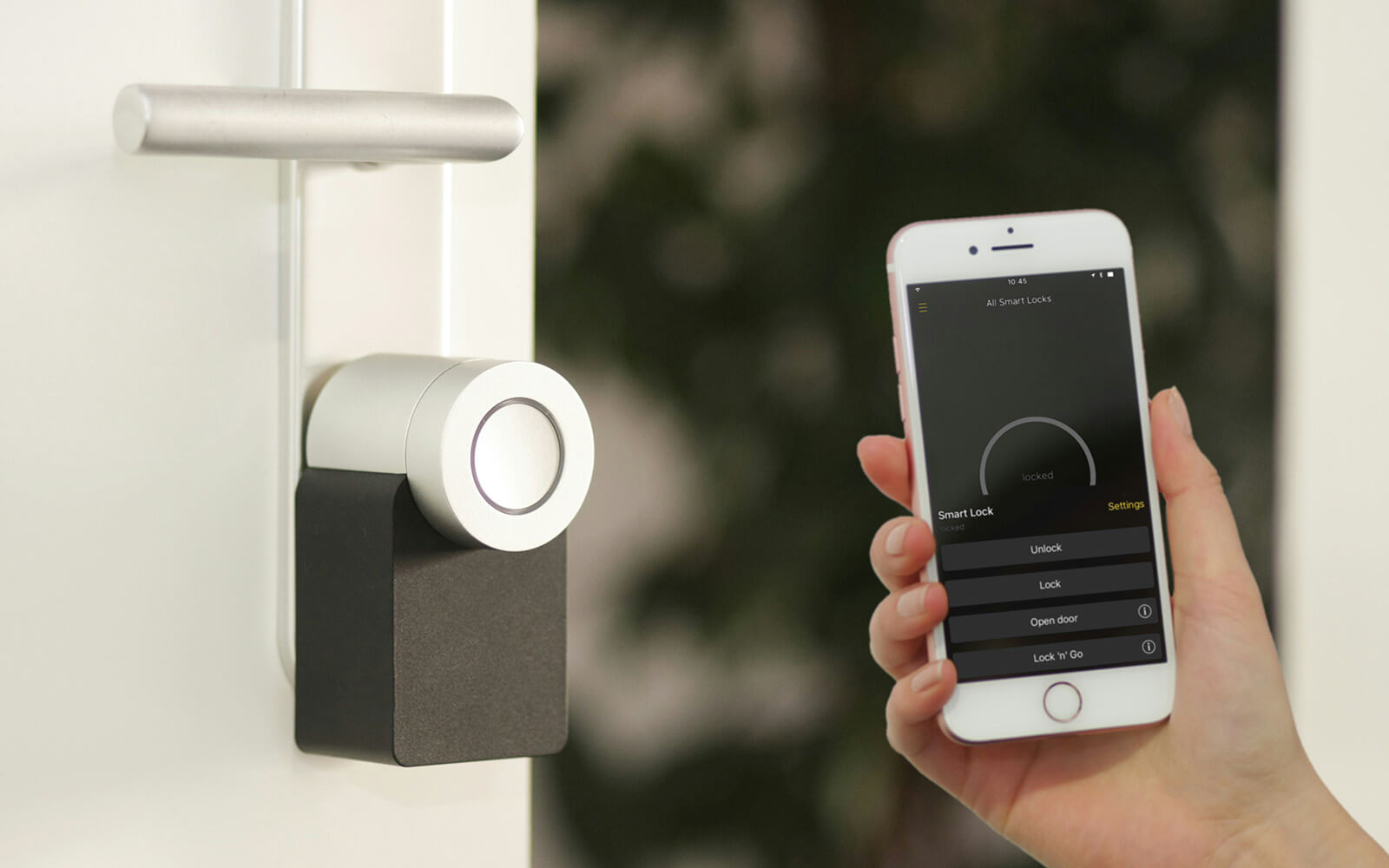
The security aspect of automated controls cannot be understated. Integrated surveillance and access control systems enhance security. They provide real-time alerts and can respond to threats instantly, minimizing potential risks.
With the potential for integration with IoT devices, these controls can also offer predictive maintenance. They can identify potential system failures before they occur, preventing costly repairs. This proactive approach to maintenance reduces downtime and extends the life of building equipment.
In summary, automated controls are not just about convenience. They are essential for sustainable building operations, offering cost savings, improved safety, and enhanced comfort. As technology advances, the importance of these systems will continue to grow.
Understanding Building Control Systems
Modern building control systems leverage advanced technologies like IoT and data analytics. This allows for real-time monitoring and control of systems. The result is a smarter building that can adapt dynamically to changing conditions. For instance, sensors detect when rooms are occupied and adjust climate controls accordingly, ensuring no energy is wasted heating or cooling empty spaces.
Communication networks form the backbone of building control systems. They enable different components to interact and share data effectively. A robust communication network ensures that systems can be monitored and controlled remotely, providing flexibility and ease of management.
Security is another critical aspect of building control systems. Integrated surveillance and access control systems enhance building safety. Real-time alerts and automated responses to security breaches reduce risks significantly.
In conclusion, building control systems are essential for modern building management. They provide the tools needed to manage various building operations efficiently. As technology evolves, these systems will become even more sophisticated, offering greater capabilities and benefits for building managers and occupants.
Types of Building Automation Systems
Building automation systems (BAS) come in various types, each tailored to specific needs and building types. The most common types include HVAC automation, lighting control systems, security systems, and energy management systems. HVAC automation focuses on regulating heating, ventilation, and air conditioning for optimal comfort and energy efficiency.
Lighting control systems automate indoor and outdoor lighting, adapting to occupancy and natural light levels. Security systems integrate surveillance and access controls, enhancing safety. Energy management systems monitor energy usage, enabling efficient consumption and lower costs. Each type serves a unique purpose, but together they create a comprehensive building automation strategy.
Components of a BAS System
A building automation system (BAS) comprises several key components working in harmony. Sensors are crucial for collecting data on temperature, humidity, occupancy, and light levels. They provide the information needed for the system to make informed adjustments. Actuators follow commands based on sensor data, controlling devices like HVAC units, lighting fixtures, and valves.
Control panels serve as the system's nerve center. They process data, run automation software, and send instructions to various building elements. User interfaces allow operators to monitor and control systems. Interfaces range from dedicated control stations to mobile applications providing easy, remote management.
Communication protocols are essential for data exchange between system components. Common protocols include BACnet, Modbus, and LonWorks, ensuring interoperability and seamless communication. Additionally, the system software plays a critical role, handling analytics, data visualization, and reporting. It enables managers to optimize performance, predict maintenance needs, and enhance efficiency.
The network infrastructure connects all these components, forming a cohesive BAS. A reliable network ensures smooth operation and real-time data flow, crucial for system effectiveness.
Role of Building Controllers
Building controllers are central elements in a BAS, acting as intermediaries between sensors, actuators, and the management interface. They process sensor data and execute control strategies to maintain desired environmental conditions. Controllers can adjust HVAC settings, modulate lighting, and operate security systems. They ensure that operations are aligned with pre-defined set points and user preferences.
Controllers also enable system integration, connecting disparate components into a unified structure. This allows for streamlined management and the sharing of real-time data across different systems.
Modern controllers support advanced functions like demand response and integration with IoT devices, offering scalable and future-proof solutions. Their flexibility and adaptability make them indispensable in creating responsive and efficient building environments.
HVAC Building Automation
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) are critical for maintaining indoor comfort. HVAC building automation focuses on optimizing these systems for efficiency and energy savings. Through intelligent automation, facility managers can regulate temperature, humidity, and airflow with precision.
HVAC automation systems respond to real-time data from sensors, adjusting settings as needed to maintain ideal conditions. This responsive approach not only enhances comfort but also reduces energy waste.
Moreover, HVAC systems integrated with building automation can predict energy needs based on historical data. This allows for smarter energy use, aligning with sustainability goals and reducing operational costs significantly.
Overview of HVAC Controls
HVAC controls are the backbone of any automated system. They regulate temperature, ventilation, and air quality, ensuring optimal indoor environments. Modern controls include programmable thermostats, smart sensors, and variable speed drives.
These components work together to adjust heating and cooling outputs based on occupancy and external weather conditions. Advanced controls facilitate zoned climate management, allowing different areas to be controlled independently. This flexibility ensures that spaces are conditioned appropriately according to use and occupancy.
Benefits of HVAC Automation
HVAC automation offers numerous benefits, making it a worthwhile investment for building owners. One key advantage is significant energy savings. Automated systems optimize usage, resulting in lower utility bills.
Another benefit is improved occupant comfort. Systems maintain consistent temperatures and good air quality, enhancing the indoor experience. This can lead to increased occupant satisfaction and productivity in commercial spaces.
Additionally, HVAC automation supports preventive maintenance. Systems can monitor their own performance and alert facility managers of issues before they escalate. This proactive approach reduces the likelihood of costly repairs and extends equipment lifespan.
Finally, HVAC automation contributes to environmental sustainability. By minimizing energy consumption, automated systems help reduce a building's carbon footprint.
Integration with Building Automation System Software
Integration with building automation system (BAS) software is crucial for HVAC automation. This integration allows different systems to operate coherently, sharing data for improved decision-making. BAS software provides a user-friendly platform for monitoring and controlling HVAC functions.
Through BAS, managers can oversee multiple systems from a single interface. This centralization streamlines operations, making it easier to implement energy-saving strategies.
The software also supports data analytics, providing insights into system performance.
These insights can guide adjustments and optimizations, ensuring that HVAC systems operate at peak efficiency. In essence, integration with BAS software transforms HVAC management into a seamless and efficient process.
Smart Lighting Solutions in Building Automation
Smart lighting is a transformative element in modern building automation systems. By integrating intelligent lighting solutions, buildings can achieve remarkable energy efficiency and enhanced user experiences. Smart lighting systems use sensors and advanced software to adjust lighting based on occupancy, time of day, and natural light availability. This leads to significant energy savings and improved indoor environments.
These systems support customizable settings, allowing users to create preferred lighting environments. This personalizes the experience, promoting comfort and productivity. In commercial settings, the right lighting can boost employee performance and satisfaction. Integration of smart lighting with building automation systems (BAS) extends its benefits further.
A central BAS platform provides facility managers with real-time data, enabling effective monitoring and management. When coupled with BAS, smart lighting contributes to a building's overall energy management strategy. This holistic approach not only optimizes resource use but also supports sustainability goals.
How Smart Lighting Works
Smart lighting systems use a network of sensors and controllers. Sensors detect motion, natural light levels, and occupancy. When changes are detected, the system automatically adjusts lights to maintain optimal conditions.
Controllers process sensor data and communicate with lighting fixtures. They can dim or brighten lights, switch them on or off, depending on the real-time scenario. Such automation removes the need for manual switches, increasing convenience.
Smart lighting can also be controlled remotely via mobile apps. Users can adjust settings from anywhere, providing flexibility and control over lighting preferences.
Benefits of Integrating Smart Lighting in BAS
Integrating smart lighting with BAS offers numerous benefits. Energy savings are perhaps the most significant. Automated adjustments ensure lights are used only when needed, reducing electricity consumption.
Another benefit is enhanced lighting control. Facility managers have access to detailed insights, allowing them to fine-tune lighting strategies. This can lead to further optimizations and cost reductions.
Furthermore, smart lighting boosts occupant comfort and well-being. By ensuring the right lighting levels at the right times, it contributes to a positive and productive indoor environment. This can have profound effects on mood and efficiency, especially in workplaces.
Finally, integration allows for better maintenance and management. Automated alerts on system performance help in addressing issues promptly, preventing disruptions.
Case Studies: Successful Implementations
Numerous case studies highlight the advantages of smart lighting in building automation. For instance, a large corporate office implemented smart lighting, reducing its lighting costs by 40%. Sensors adjusted lighting based on occupancy, limiting waste and ensuring comfort.
In another example, a university campus deployed an integrated lighting system across its facilities. This led to improved security, as motion-activated lights deterred unauthorized access. The campus also achieved significant energy savings, aligning with its sustainability initiatives.
These implementations demonstrate smart lighting's potential to transform environments, save energy, and enhance user experiences. As technology advances, more buildings are expected to adopt these intelligent solutions, reaping both economic and environmental benefits.
Building Automation Technology Trends
The realm of building automation is rapidly evolving, driven by technological innovations. These advancements are reshaping how we manage and interact with buildings. From energy efficiency to increased occupant satisfaction, technology trends are opening new possibilities for smarter building management. The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and advanced analytics is at the forefront of these changes.
IoT has enabled deeper connectivity within building systems. Devices can communicate and share data in real time, improving system responsiveness and efficiency. AI further amplifies this connectivity by analyzing data to provide actionable insights. This combination supports predictive maintenance and real-time optimization, reducing downtime and operating costs.
Advancements in building automation networks and software mean better integration of systems, enhancing functionality and user experience. As these technologies mature, they pave the way for seamless communication across different platforms, ensuring buildings remain adaptive and efficient.
Emerging Technologies in Building Automation
Several emerging technologies are enhancing building automation systems. Wireless technology is one crucial development, offering flexibility in system setup and modification. It simplifies installations, particularly in retrofit projects, and reduces costs associated with extensive cabling.
Cloud computing is another game-changer, providing scalable storage and computing power for BAS data. This technology ensures data is readily accessible and secure, enabling remote monitoring and management.
Furthermore, machine learning algorithms are increasingly being deployed within BAS. These algorithms predict system needs based on historical data, allowing for better resource allocation and reduced energy consumption. The result is a more intuitive and efficient building that learns and adapts over time, making maintenance more proactive and less reactive.
The Future of Smart Building Controls
Looking ahead, the future of smart building controls is promising and expansive. One emerging trend is the increased integration of AI to enhance system intelligence and autonomy. With AI, systems will not only respond to inputs but also anticipate future requirements, offering a truly adaptive environment.
Additionally, the convergence of IT and operational technology will continue to grow. This integration allows for comprehensive data utilization, supporting smarter decision-making processes. As a result, building controls will become more sophisticated, yet user-friendly.
Sustainability will also drive innovation in smart building controls. Future systems will likely focus on resource conservation and integration with renewable energy sources.
These advanced solutions will not only optimize energy use but also support broader sustainability goals, contributing to greener, more efficient urban infrastructures. As technology progresses, the potential for smart building controls will extend beyond buildings, influencing larger smart city initiatives.
Leading Building Automation Companies
The building automation industry is populated with influential players driving significant innovations. Building automation companies are key to advancing intelligent building systems. They develop solutions for energy management, security, and occupant comfort across various buildings. These companies offer a range of technologies tailored to meet diverse building needs.
Industry leaders include Siemens, Johnson Controls, and Honeywell. Each company has established a strong reputation for producing reliable and cutting-edge BAS solutions. They emphasize scalability, efficiency, and integration, which are critical for modern buildings. These firms not only contribute technological know-how but also bring decades of industry experience.
Additionally, smaller firms are making an impact by offering specialized solutions. These companies focus on niche markets or offer unique features that set them apart. Their innovative approaches often challenge established practices, pushing the industry forward. Partnerships with tech firms drive further advancements, indicating a collaborative future.
Overview of Top Building Automation Companies
Several top companies dominate the building automation sector, recognized for their advanced solutions and market influence. Siemens is a global leader, renowned for its comprehensive and integrated BAS systems. Their solutions cater to a wide array of sectors, from commercial buildings to industrial facilities.
Johnson Controls also holds a significant position with its extensive range of BAS products. Their focus on sustainable and smart building technology aligns with growing demands for eco-friendly solutions. This alignment helps them stay ahead in a competitive market.
Honeywell is another prominent name, excelling in automated building controls and integrated solutions. Known for their focus on user-friendly BAS software and robust systems, they cater to diverse client needs. These top companies continually innovate, defining standards and leading industry trends.
Comparison of Building Automation Systems
When comparing building automation systems from leading companies, several factors come into play. Scalability is crucial, as systems must accommodate growing building needs. Siemens, for instance, offers highly scalable solutions that adapt to different building sizes and types.
Ease of integration is another vital aspect. Johnson Controls excels here, with systems that seamlessly integrate with existing building infrastructures. This integration ensures smooth transitions from older systems to modern automated controls.
Feature sets vary significantly between systems. Honeywell stands out with advanced features, such as intuitive user interfaces and extensive data analytics capabilities. While each company brings unique strengths, the best choice often depends on specific building requirements and organizational goals. Evaluating these factors can help stakeholders make informed decisions when selecting a BAS provider.
Conclusion
Building automation systems transform how buildings operate. From HVAC control to smart lighting, these systems enhance efficiency and comfort. They offer significant energy savings and improve building management.
Key components include sensors, control panels, and user-friendly software. Industry leaders like Siemens and Honeywell set high standards with innovative solutions. The integration of IoT, AI, and data analytics points to a future rich in possibilities.
Summary of Key Points
Building automation systems deliver energy efficiency and improved comfort. Leaders like Siemens provide scalable solutions. Key features include user-friendly interfaces and advanced analytics. Industry trends favor smart integration and enhanced building management. These systems redefine how we interact with our environments.
Future Outlook for Building Automation
As technology advances, building automation will become more integral. Future systems will integrate AI and IoT more deeply, enhancing capabilities. Continuous innovation and collaboration will foster smart, sustainable infrastructure. This evolution will redefine building experiences and advance urban development.
CLICK BOARDS FOR SMART HVAC AND LIGHTING CONTROL
Click boards™ are designed to simplify the development of embedded systems in building automation. Whether you’re developing HVAC control systems, smart lighting, or environmental monitoring, the wide selection of Click boards enables rapid prototyping and seamless integration of sensors, actuators, and communication interfaces.
For example, temperature and humidity sensor Click boards are essential in smart HVAC designs, while ambient light and motion sensor boards are ideal for intelligent lighting control. Combined with relay, motor control, and wireless connectivity boards, these modular solutions cover all key functionalities in modern automated buildings.
EASY INTEGRATION FOR CUSTOM AUTOMATION DESIGNS
By combining multiple Click boards, engineers can quickly build tailored building automation solutions that scale. The boards in the grid below are hand-picked for projects involving temperature regulation, lighting management, occupancy detection, and remote system access. All of them plug into development boards via the mikroBUS™ socket—no soldering or additional wiring required—making development faster, cleaner, and more adaptable to evolving needs.
EXPLORE REAL-WORLD PROJECTS ON EMBEDDEDWIKI
To see how Click boards™ are used in real applications, head over to EmbeddedWiki — MIKROE’s dedicated project hub. You'll find ready-made automation projects built around the Click boards featured in this blog. From smart thermostats and automated blinds to motion-based lighting systems, each project includes source code, schematics, and direct links to the required boards.
EmbeddedWiki makes it easy to replicate, customize, or expand building automation setups using modular embedded hardware. It’s an ideal resource for developers looking to move from concept to prototype quickly and efficiently.
ABOUT MIKROE
MIKROE is committed to changing the embedded electronics industry through the use of time-saving industry-standard hardware and software solutions. With unique concepts like Remote Access, One New Product/Day, Multi-Architectural IDE and most recently, the EmbeddedWiki™ platform with more than million ready-for-use projects, MIKROE combines its dev boards, compilers, smart displays, programmers/debuggers and 1850+ Click peripheral boards to dramatically cut development time. mikroBUS™; mikroSDK™; SiBRAIN™ and DISCON™ are open standards and mikroBUS only has been adopted by over 100 leading microcontroller companies and integrated on their development boards.
Your MIKROE